Industry preferred Fortran, academics preferred Algol
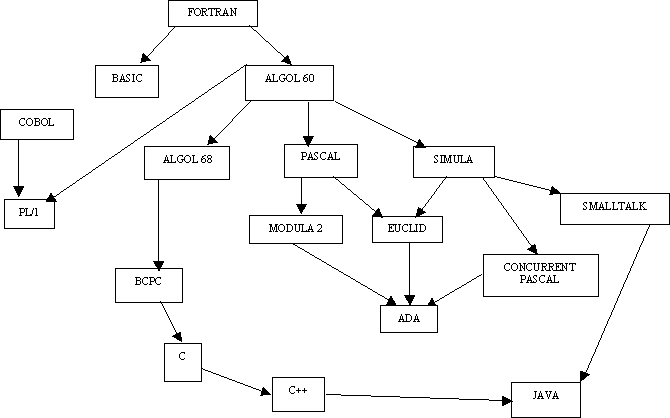
ALGOL 68 (1968-1975)
- Was very different from its predecessor
- Most interesting feature was orthogonality
- Includes user-defined data types
- Introduced the kind of dynamic arrays that are termed implicit heap-dynamic,
(in ALGOL 68, dynamic arrays are called flex arrays).
- Orthogonality of features, (combining simple features to create new ones)
"Formal definition" (semantics)
Pascal, developed by Niklaus Wirth in 1968 (very popular 1975-90)
The
language guide to Pascal
- By mid 70's, Pascal became very widely used
- Had been designed specially for teaching programming
- Has remarkable combination of simplicity and expressively
- Compile relatively efficient code
- Relatively safe language
- User defined data types
- Axiomatic definition (syntax in BNF)
- Negative features included:
- Enumerated types had implicit order
- Pointers allowed dangerous practices
- No dynamic array bounds
- Complete compile time error checking not possible
- Lack of string processing
Ada- 1980
The
language guide to Ada
- Grew out of Pascal
- Primary goal: Dept. of Defense wanted to support
programming of embedded systems
- Named after Ada Byron - world's first programmer
- Abstract development
- Exception handling
- Parallel processing
- Program modularity, portability, extensibility
C- 1972
The
language guide to C
- Influenced by Algol 68
- Allows bit-level operations
- Treatment of pointers
- People who like C like its flexibility and those who don't
like C find it too insecure
- C is part of the widely used UNIX operating system
- Weakness: no type checking
COBOL developed in 1959--one of the earliest languages
The language guide to COBOL
- 1959 Dept. of Defense wanted a single language
- 1960 Remington (Rand) developed the first compilers
- Machine independent
- General if/then else
- 'Noise' words (almost English-like, so lowly accountants could
follow programs i.e. they didn’t have to know how to program to
know what the code represented)
PL/1 mid-60's
The language guide to PL/1
IBM designed to replace FORTRAN & COBOL, (and Algol, to a certain extent)
- Represents the first large scale attempt to design a
language that could be used for a Broad spectrum of application areas
- Developed as an IBM product
- Block structure
- Recursive procedure
- COBOL-like records
- Exception handling
- Multi-tasking
- Pointers were included as a data type
- Cross section of arrays could be referenced
- It was considered at partial success
- Significant uses in business and scientific applications. Imperative languages
Functional languages
LISP
The
language guide to LISP
- Developed at MIT, (and others) by John McCarthy; AI is its application domain
- Symbolic expression, able to manipulate variable names like
variable values (i.e. pointer arithmetic)
- Uniform representation for expressions (i.e. executable data structures.)
- New form of conditional expression (similar to "switch" statements)
- Pre-fix expressions- operator followed by arguments
- Recursion more widely used
- "Garbage collection" A "linked-list" type of structure is the basic structure in LISP
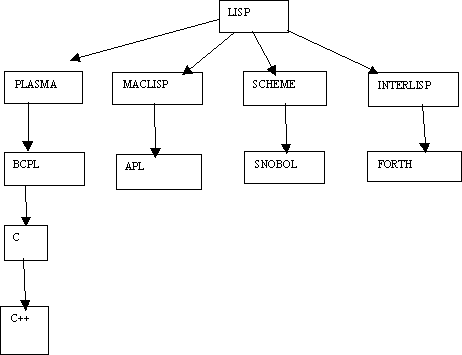
APL was developed at IBM in 1960 by Ken Iverson
he
language guide to APL
- Very compact notation for computation
- Provided for much matrix manipulation
- NOT Algol-like in nature
- Originally built to describe specifications of IBM360
Snobol-1964
the language guide to snobol
- It was designed specially for text processing (string
processing) Cobol and Fortran were poor string processors
- Is a collection of powerful operations for string pattern matching
- One of the early applications was for writing text editors
- Can have strings of infinite length.
Rule-Based languages
Prolog- 1975
The
language guide to prolog
- The name Prolog comes from PROgramming LOGic
- Programming in logic programming language is non-procedural
- The primary components of Prolog are a method for specifying
predicate calculus propositions and an implementation of a restricted
form of resolution
- Logic programming is not very inefficient
- Logic programming has a narrow domain
OO languages
C++ (C with objects)
the
language guide to C++
- Object oriented programming
- Standardized » 1990
- Bjarne Stroustrup at Bell labs
- Evolved from C
- Includes: derived classes, public/private access of
inherited components, constructor and destructor functions, friend
classes, and virtual functions
- Includes templates and exception handling
- Operators and functions can be overloaded
- Popular because of availability of good and expensive compilers
- Weaknesses: inherited many of the C insecurities which makes
it a less safe language.
Smalltalk- 1980
the
language guide to Smalltalk
- Object-oriented programming
- Objects are structures that encapsulate local data and a
collection of operations called methods that is available to other objects
- Smalltalk world is populated by nothing but objects, from
integer constants to large complex software systems
- Dynamic type binding
- Unit control, taken from simulation world
- Objects - communicate with each other by message passing